Apr 6, 2023
Apr 6, 2023All About EITC: Who is Eligible to Receive and Critical Information to Consider.
Americans who are either self-employed or wage earners may be eligible for a tax break known as Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). Over 25 million taxpayers claim it each year, yet many people are unsure whether they qualify or why. This article will cover who is eligible to receive EITC and what you should know before filing your taxes. Also make sure to get in touch with your dedicated free tax expert today!
Are you aware of the benefits of Earned Income Tax Credit?
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is an incentive issued to people with an earned income that meets certain criteria. It provides a reduction in your tax bill, dollar-for-dollar. Although there are other prerequisites, these are relatively straightforward and easy to understand.
It applies to earnings from tax form W-2 or tax form 1099.
Any money received as a result of work is considered “earned income”, which can come in the form of wages from an employer via a W-2 form or earnings through self-employment with 1099.
It’s refundable
The earned income credit doesn’t just lower your taxes but pays you back as well. This is known as the refundable amount – that being, should the credit be greater than what you owe in tax, you’ll receive a refund for the difference.
Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) tax credit is for low and moderate-income families and individuals.
Designed to provide financial relief, the low-to-moderate-income worker’s and family’s credit seeks to help those struggling to make a living wage. Primarily intended for individuals attempting to support their households on an insufficient income, this tax break can be an invaluable asset.
Who is eligible for the EITC?
Want to know if you are you eligible for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)? To find out, take a look at the following requirements from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS):
– You need to have earned income in the form of wages or self-employment income. The amount should be no less than $1.
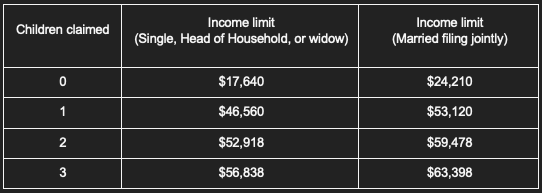
– Your adjusted gross income should be at most $59,187 in 2022 (the amount may vary depending on your filing status and a number of dependants).
– Investment income must reach at most $10,300 this year.
– A valid Social Security number is required.
– Not filing Form 2555
First Requirement: Earned income from working
When it comes to earned income, this includes wages, salaries, tips, and any net income generated from self-employment activity. For freelancers who are employed full-time, this kind of income is able to be claimed via the EITC regardless of what type of profit – even as small as $1 – was made. However, the credit is calculated based on your post-deduction net earnings.
Let’s imagine that you own a web store and have earned a total of $10,000 from sales over one year. The cost to run your business amounted to $3,000:
– Purchasing stock
– Paying platform fees
– Ensuring photography for the products
– Organizing and sending out orders…etc.
By subtracting these expenses, you are left with a net income of $7,000.
What doesn’t count as earned income?
In contrast to earned income, unearned income does not qualify for the EITC (Earned Income Tax Credit). This is because unearned income includes such sources as investments, dividends, stock sales, passive incomes like rents or royalties, and government benefits. Consequently, relying exclusively on these sources would mean being ineligible for the Earned Income Tax Credit.
Second Requirement: Adjusted gross income must be below a specific limit.
The second criterion for eligibility is having an adjusted gross income below a predetermined level. This figure represents your overall income minus any deductions, such as student loan interest, retirement contributions, and health insurance payments for self-employed individuals. It serves to lower your taxable income.
How the income limit for the Earned Income Tax Credit works?
Establishing the income threshold for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). In order to be approved to receive the Earned Income Tax Credit, you need to consider a couple of factors.
For those filing jointly with three children, a maximum of $59,187 is allowed. Yet, those who file singly, as heads of households or widows, may find their threshold much lower than that. Similarly, couples without kids or those with only one or two may also experience decreased income limits.
2022 Income Limit for EITC:
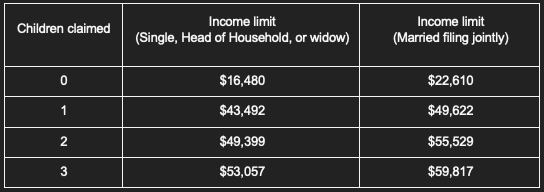
2023 Income Limit for EITC:
Third Requirement: Investment income must be under a specific limited amout.
To meet Requirement #3, your investment income must remain beneath a certain level. This consists of taxable and tax-exempt interest as well as capital gain distributions. It is important to remember that when calculating your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI), investment income is included in the total. Therefore, your overall income needs to stay under the threshold for your individual situation, but also make sure that your investment income is at most $10,300 for 2022 or $11,000 for 2023.
So how does AGI and other investment income work together towards your eligibilty for EITC?
Explaining the Relationship between AGI and Investment Income Limits
Here’s an example. A single mother with one child has an income limit of $43,492. Let’s say she has a total income of $30,000; her eligibility for the EITC would depend on where this number comes from:
– She will qualify for the credit is her income is entirely from earned sources such as a day job or freelance hustle.
– She will still be eligible with $29,000 in earned income plus an additional $1,000 in investment income.
– However, she will not qualify with lesser earnings ($20,000) combined with a higher investment yield ($30,000); even though the AGI limit is met here, being over the investment limits disqualifies her.
Fourth Requirement: A valid Social Security number
When filing, taxpayers who provide an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) or Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number (ATIN) will not be eligible for the credit. Sadly, this prevents undocumented citizens from availing of the reward. Furthermore, to claim the benefit, a married couple must be US residents or citizens.
Can you still claim the EITC if you were a US citizen or a resident for a fraction of the year?
Are you married, and only one of you has been a US resident for the whole year? You may be eligible to claim the EITC, depending on the circumstances. In order to qualify, your spouse must have been present in the United States for at least six months that same year. This usually transpires when moving into or out of the country.
Fifth Requirement: Not filing Form 2555
This document informs the IRS about foreign earnings that may be exempt from US taxes. The Foreign Income Exclusion can be claimed when a taxpayer’s “tax home” is located abroad and their taxes are paid to another country instead of America.
Tags:
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked*


Don’t Miss Any Updates
Sign up with your email to receive latest updates.





 admin
admin No Comments
No Comments